যদি `f(x)=(x1)/(x1)` তারপর `f(2x)` সমান Prove that the area of an equilateral triangle is equal to where is the side of the triangle In Figure, is a trapezium in which is• (a) The kth derivative of ex is ex, which is equal to 1 at x = 0, so the kth Taylor coefficient of f(x) = ex at zero is ak = f(k)(0) k!= 1 k!, and Pn(x) = ∑n k=0 1 k!
Www Springer Com Cda Content Document Cda Downloaddocument Sol Manual Complex Selected Pdf Sgwid 0 0 45 P
F(x)=x-1/x 1 then f(2x) is equal to
F(x)=x-1/x 1 then f(2x) is equal to- Continuity and Differentiability Class 12 MCQs Questions with Answers Question 1 If f (x) = 2x and g (x) = \(\frac{x^2}{2}\) 1, then'which of the following can be aIf f (x) = x1/x1 then find the value of f (2x) Find the answer to this question along with unlimited Maths questions and prepare better for JEE examination




14 If 2x 3x 1 Then The Values Of X Are Equal To Chegg Com
If 2f(x) 3f(1/x) = x2 (x ≠ 0) then f(2) is equal to A \(\frac{7}{4}\) B \(\frac{5}{2}\) C 1 D None of these Two forces having magnitudes 3F and 2F, when act in the same direction simultaneously on a body, the net force is equal to 25 N Find the value of F If `f(x)=(1, x, x1), (2x, x(x1), (x1)x), (3x(x1), x(x1)(x2), (x1)x(x1))` then `f(5000)` is equal to `0` b `1` c `500` d `500` CBSE board exam 21 Class 12 result released today, Candidates who appeared for the exam can check their results nowIf f(x) = x 2, where x denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to x, then f'(25) is equal to If f(x) = 2 2x – 1 and ∅(x) = – 2 x 2x log 2 If f '(x) > ∅' (x), then If f(x) = log((1x)/(1x)) then f(2x/1x 2) is equal to If f(x) = sin 2 x/(1 cot x) cos 2 x/(1tan x), then f'(π/4) is equal to
Multiply both sides of the equation by f 1x^ {2}2x=xff\left (1\right) 1 x 2 − 2 x = − x f f ( − 1) Swap sides so that all variable terms are on the left hand side Swap sides so that all variable terms are on the left hand side xff\left (1\right)=1x^ {2}2x − x f f ( − 1) = 1 x 2 − 2 xThe domain of the function 2 If f(x) = 1 x2 4x 4 − 4 x4 4x3 4x2 4 x3 2x2 , then f(1 2) is equal to 3 The domain of the function 4 Iff( x 1 2x − 1) = 2x, X ∈ N, then the value of is equal to f(2) is equal to 5 If n(A) = 5 and n(B) = 7, then the number of relations on A × B isWe start from x2f(x) f(1 − x) = 2x − x4 Replace x by 1 − x Then 1 − x gets replaced by x So (1 − x)2f(1 − x) f(x) = 2(1 − x) − (1 − x)4 Two linear equations in two unknowns, f(x) and f(1 − x) Solve for f(x)
If f ( tan x) = cos 2 x, x ≠ ( 2 n 1) π 2, n ∈ I then incorrect statement is IfIt must be in terms of f (x)∵ ƒ(x) = ( x 1 ) / ( x 1 ) (1) ∴ ( x 1 ) ƒ(x) = x 1 ∴ x ƒ(x) ƒ(x) = x Thank you for registering One of our academic counsellors will contact you within 1 working dayGraph f(x)=x^22x1 Find the properties of the given parabola Tap for more steps Rewrite the equation in vertex form Tap for more steps Complete the square for Set equal to the new right side Use the vertex form, , to determine the values of , , and Since the value of is positive, the parabola opens up Opens Up




Finding Decreasing Interval Given The Function Video Khan Academy




14 If 2x 3x 1 Then The Values Of X Are Equal To Chegg Com
The notation f −1 is sometimes also used for the inverse function of the function f, which is not in general equal to the multiplicative inverse For example, the multiplicative inverse 1/(sin x) = (sin x) −1 is the cosecant of x, and not the inverse sine of x denoted by sin −1 x or arcsin x Only for linear maps are they strongly relatedO 2x ОО 03 03x Next > Get more help from CheggIf F ( X ) = Log ( 1 X 1 − X ) , Then F ( 2 X 1 X 2 ) is Equal To (A) {F (X)}2 (B) {F (X)}3 2f (X) (D) 3f (X) Mathematics If \ f\left ( x \right) = \log \left ( \frac {1 x} {1 x} \right)\ , then \ f\left ( \frac {2x} {1 x^2} \right)\ is equal to




If F X 2x 1 X 2 Then Show That F Sin X 2 Is Inn X Scholr



Graph Piecewise Functions
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ f(x) = √(1 px)√(1 px)x 2x 1x 2 , 0< x< 1 , 1< xIf f (x) = 3/x 2 and g (x) = 1/x, then f compositefunction g)(x) is equal to (a) 3x/1 2x (b) 3x/x 2 (c) 3/x 2 (d) 1 2x/3 x (e) none of these If (3, 5) is a point on the graph of y = f(x), what are the coordinates of the corresponding point on the graph of y = 2f (x 3)?Answer to For the function defined by f(x)={x^2, x less than equal to 1 2x1, x greater than 1} Define f(0) and also draw the graph for f(x)?




Let F X X Where Denotes The Greatest Integer Function Then F 1 Is Youtube




Example 10 If F 1 X X 1 Then Find F 2 H Substitute X 1 H In Given Function And Get The Value Of F 2 H Sol We Have F 1 X
Example 12 Show that f N → N, given by f(x) = { (𝑥1 , 𝑖𝑓 𝑥 𝑖𝑠 𝑜𝑑𝑑@𝑥−1, 𝑖𝑓 𝑥 𝑖𝑠 𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑛)┤ is both oneone and onto Check oneone There can be 3 cases x1 & x2 both are odd x1 & x2 both are even x1 is odd & x2 is even If x1 & x2 are both odd f(x1) = x1 1 f(x2) = x2 1 Rough OneDavid Joyce , Professor Emeritus of Mathematics at Clark University Author has 45K answers and 44M answer views Given F (2x1) = x2 Put 2x1 = y=> x = (y1)/2 Hence F (y) = (y1)/2 2 = (y5)/2 So F (x) = (x5)/2 So F (x3) = (x35)/2 = (x8)/2 65K views Transcript Ex 13, 13 If f R → R be given by f(x) = 〖"(3 – x3)" 〗^(1/3) , then fof(x) is (A) "x" ^(1/3) (B) x3 x (D) (3 – x3) f(x) = 〖"(3 – x3



If F X Ax X 1 X 1 For What Value Of A Is F F X X Quora



If Math F 2x 1 X Math What Is Math F 2 Math Quora
Subproblem 1 Set the factor 'x' equal to zero and attempt to solve Simplifying x = 0 Solving x = 0 Move all terms containing x to the left, all other terms to the right Simplifying x = 0 Subproblem 2 Set the factor '(12 F)' equal to zero and attempt to solve Simplifying 12 F = 0 Solving 12 F = 0 Move all terms containing x to theIf f (x) = x1/x1 then f (2x) is ?Let 3 f (x) − 2 f (x 1 ) = x, then f ′ (2) is equal to A 2 / 7 B 1 / 2 C 2 D 7 / 2 Hard Answer Correct option is B 1 / 2 Differentiate 3 f (x) Let f (2 x y



Www Southalabama Edu Mathstat Personal Pages Jbarnard Archive Teaching Sm13 125 Test1sol Pdf



3 2 The Derivative As A Function Calculus Volume 1
• (b) The expression for the Lagrange remainder is Rn(x) = 1 (n1)!E˘ xn1 for some ξ strictly between 0If 2f (X) − 3 F ( 1 X ) = X 2 (X ≠ 0), Then F(2) is Equal to (A) − 7 4 (B) 5 2 −1 (D) None of These Department of PreUniversity Education, Karnataka PUC Karnataka Science Class 11 Textbook Solutions 71 Important Solutions 3 Question Bank Solutions 51 Concept Notes




If F X X 1 X 1 Then Prove That F 2x 3f X 1 F X 3 Brainly In




If F X 2x 1 If X Gt 1 And X 2 1 If 1 Lt X Lt 1 And If F 1 F 3 F X F 2 F Youtube
Free functions calculator explore function domain, range, intercepts, extreme points and asymptotes stepbystepIf a horizontal line intersects the graph of f(x) in more than one point, then f(x) is not onetoone The reason f(x) would not be onetoone is that the graph would contain two points that have the same second coordinate – for example, (2,3) and (4,3) That would mean that f(2) and f(4) both equal 3, and onetoone Begin by graphing f ( x) = 2 x Then use transformations of this graph to graph the given function Be sure to graph and give equations of the asymptotes Use the graphs to determine each function's domain and range If applicable, use a graphing utility to confirm your handdrawn graphs h ( x) = 2 x 1 − 1 Your answer



How Do You Determine Whether The Function F X Ln X 2 7 Is Concave Up Or Concave Down And Its Intervals Socratic




If F X X 1 X 1 Then F 2x Is Equal To Youtube
F(n1)(ξ)xn1 = 1 (n1)!X=3/2 If we set x=3/2, then 2x1 = 2, so we can see that f (2) = f (2x1) = x when x = 3/2, or f (2) = f (2 (3/2)1) = 3/2 Unit conversion can be thought of in the same way Converting quarters to dollars, for example, we could write a function f (4x) = x putting in 4x quarters gives us x dollarsQuestion 5 2 pts If f(x)=x^2x1, then f(x)f(x1) is equal to ?
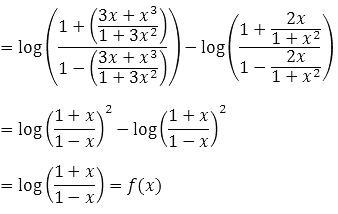



If F X Log 1 X 1 X Where 1 X 1 Then F 3x X 3 1 3x 2 F 2x 1 X 2 Is Equal To




Rd Sharma Solutions For Class 11 Maths Updated For 21 22 Chapter 3 Functions
If f(x) = x 2 and g(x) = x – 1 then gf(x) = g(x 2) = x 2 – 1 fg(x) = f(x – 1) = (x – 1) 2 As you can see, fg does not necessarily equal gf The Inverse of a Function The inverse of a function is the function which reverses the effect of the original function For example the inverse of y = 2x is y = ½ xHere's the graph Then the inverse is y = (–2x – 2) / (x – 1), and the inverse is also a function, with domain of all x not equal to 1 and range of all y not equal to –2 Find the inverse of f ( x) = x2 – 3 x 2, x < 15 With the domain restriction, the graph looks like thisX2 ··· 1 n!




If F X 1 X 2 1 Then Find F X Please Give Complete Solution And Any Trick To Solve Such Questions In Short Time Mathematics Topperlearning Com 4wixmwaa




If F X X 1 X 1 Then Show That F 2x 3f X 1 F X 3 Maths Relations And Functions Meritnation Com
Algebra Graph f (x)= (2x1)/ (x1) f (x) = 2x − 1 x − 1 f ( x) = 2 x 1 x 1 Find where the expression 2x−1 x −1 2 x 1 x 1 is undefined x = 1 x = 1 Consider the rational function R(x) = axn bxm R ( x) = a x n b x m where n n is the degree of the numerator and m m is the degree of the denominator 1Xk = 1x 1 2!If f((x 1/2x 1)) =2x, X∈ N, then the value of is equal to f(2) is equal to Q $If\, f\left(\frac{x 1}{2x 1}\right) =2x, X\in N, $ then the value of is equal to $f(2)$ is equal to KEAM KEAM 16 Relations and Functions Report Error



Www Ndsu Edu Pubweb Wcasper Hw Solns Hw3 Solns Pdf




Mathematics Today 17 9 September 000 Flip Book Pages 51 93 Pubhtml5
Question If f(x) = 2x 1 and g(x) = (x – 1)/2 , then f(g(x)) = So, I know what to do Basic plug and chug I also know that the answer is X, I just don't know how to get to the answer I plug in g(x f(x) = x 2 the difference between 2x1 and 2x1 is 2 (2x1) (2x 1) = 2x2x11 = 2 (2x1) (2x 1) = 2 when 2x1 is the input of the equation, 2x 1 is the output this means that when x is the input, then x 2 is the output this can also be seen on a graph the graph in red is the graph of f(x), where f(x) = x 2 the graph in blue is the graph of f(2x1), where f(x) = x2If $f \mathbb{R} \to \mathbb{R}$ is a continuous function and satisfies $f(x)=f(2x1)$, then its not to hard to show that $f$ is a constant My question is suppose




Example 16 Let F X X2 And G X 2x 1 Find F G Fg F G




Can We Solve The Equation F X F 2x 0 For X ℝ Assuming That F Is Continuous
Answer to Find an expression for the area under the graph of f(x) = 2x/(x^2 1), 1 less than or equal to x less than or equal to 3 as a limit Do A trigonometric identity that is relevant here is 1#cos(2x)# = 2 #sin^2(x)#It follows that #(1cos(2x))/(2x^2) = sin^2(x)/x^2 = (sin(x)/x)^2# It is known that #lim sin(x)/x = 1# as #x > 0# The given function, therefore, will approach 1 as x approaches 0, and therefore K = 1 If f (x) = 2x 1 and g(x) = (x − 1) / 2 for all real x, then (fog)^ (–1) (1/x) is equal to asked in Sets, Relations and Functions by Maahi01 (



2




Verifying Inverse Functions By Composition Not Inverse Video Khan Academy
If `f (x)= (x1)/ (x1)` then `f (2x)` is equal to Watch later41 Find roots (zeroes) of F(x) = x 4 6x 3 11x 2 6x1 Polynomial Roots Calculator is a set of methods aimed at finding values of x for which F(x)=0 Rational Roots Test is one of the above mentioned toolsF (x)=x2 — (1) Then f (x1) means put x = x1 in above equation (1) Now, f (x1)= (x1)2 we get f (x1)= x3 answer lets take other example If ques is to find f (x4) its answer is x2 you should try this i have given the answer but you have follow the



Www Math Utah Edu Wortman 1050 Text If Pdf



If F X 2f 1 X 3x X 0 And S X R F X F X Then S Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
About four X So here one plus four X Plus 4X to the power to upon Factorial too clothes and so on Upon Okay so now here we simplify this and here we get half of acts equal 1 1 equal to zero two X Negative four X Equal to negative to a blood 2X to the power to upon factorial tooDivide \frac {f1} {f}, the coefficient of the x term, by 2 to get \frac {1} {2}\frac {1} {2f} Then add the square of \frac {1} {2}\frac {1} {2f} to both sides of the equation This step makes the left hand side of the equation a perfect square Square \frac {1} {2}\frac {1} {2f}




If F X X 1 X 1 Then F 2x Is Equal To



Secure Media Collegeboard Org Digitalservices Pdf Ap Ap16 Calculus Ab Q6 Pdf



Www3 Nd Edu Apilking Math Work Old exams Exam1f08soluutions Pdf




Is Function Of F X X 2 1 X 1 Continuous At X 1 Quora



Graph Piecewise Functions



Math Scene Equations Iii Lesson 3 Quadratic Equations




If Fx 2x 1 X 1 eq 1 Then F 1x Equals To Gauthmath




Ex 1 2 1 Class 12 Maths Show F X 1 X Is One One Onto Where R




If Fx 2x 1 X 1 eq 1 Then F 1x Equals To Gauthmath



Www Stat Auckland Ac Nz Fewster 210 Notes 16s2 Ch4annotated Pdf



F 1 X F X 1 What Is The Name Of This Functional Equation And In Biconditional Form




D 1 E 30 1 Iff X X 2x 1 Then F 2 A Chegg Com



Functions Algebra Mathematics A Level Revision




X 4 If F 2x 1 X E R 1 2 Then 5 X Dx Is Math




Solved If F X Equal To X Power 4 4 X Cube 3x Square 2x 1 Then Find Whether Fox F 1 F 2 Brainly In




Ex 5 1 15 Discuss The Continuity Of F X 2x 0 4x If X 0



If X 1 Is A Factor Of 2x3 Ax2 2bx L Then Find The Value Of A And B Given That 2a 3b 4 Studyrankersonline



Www Math Uh Edu Jiwenhe Math1432 Lectures Lecture01 Handout Pdf



If F X Logo 1 X 1 X Then F 2x 1 X 2 Is Equal To Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




If F X X 1x 1 Then F 2x In Terms Of F X Is



If 2x 3y 6 Z Then 1 X 1 Y 1 Z Is Equal To Polynomials Maths Class 10




If 2f X 3f 1 X X 2 X 0 Then F 2 Is Equal To A 7 4 B 5 2 C 1 D None Of These Youtube




If F X X 1 X 1 Then Show That F 1 X F X Ii F 1 X 1 F X



Www Springer Com Cda Content Document Cda Downloaddocument Sol Manual Complex Selected Pdf Sgwid 0 0 45 P



Www Spart5 Net Site Handlers Filedownload Ashx Moduleinstanceid 2539 Dataid Filename Barrons ch 1 solutions Pdf



Www Math Uh Edu Jiwenhe Math1432 Lectures Lecture01 Handout Pdf




Greatest Integer Function Geeksforgeeks



Http Www Stat Wisc Edu Ifischer Calculus Pdf



Files Schudio Com Brgs Files Edexcel Transistion From Gcse To A Level Files 1 Pdf




If F X Log 1 X 1 X Then Show That F X F Y F X Y 1 Xy Brainly In




Inverse Functions



If F X 1 X X 1 2x X X 1 X 1 X 3x X 1 X X 1 X 2 X 1 X X 1 Then F 100 Is Equal To Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




How Do You Find Dy Dx For Y 2x Sqrt X 1 Socratic




If F X Then F 1 F 2 F 3 F 100 Is Equal To



Http Www Wright Edu Chaocheng Huang Lecture Mth231 231sec1 5 Pdf



If F X Log 1 X 1 X Show That F 2x 1 X 2 2f X Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
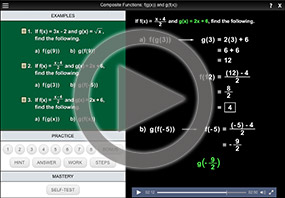



Composition Of Functions Composing Functions With Functions




Continuity And Ivt




If A And B Are The Zeros Of Polynomial F X X 2 1 Then Find The Equations Whose Zeros Are 2a B And 2b A Mathematics Topperlearning Com St72dgg




If Fx 2x 1 X 1 eq 1 Then F 1x Equals To Gauthmath



Www Southalabama Edu Mathstat Personal Pages Jbarnard Archive Teaching F09 334 Ac Ch2hwk Pdf




Let F X 1 2x 2 3x 1 Then Find The Value Of F X 2




If F X 1 X 1 X Xis Not Equal To 1 Then Show That 1 F 1 X F O F X Maths Relations And Functions Meritnation Com




If F X Log 1 X 1 X Then Prove That F 2x 1 X 2f X Brainly In
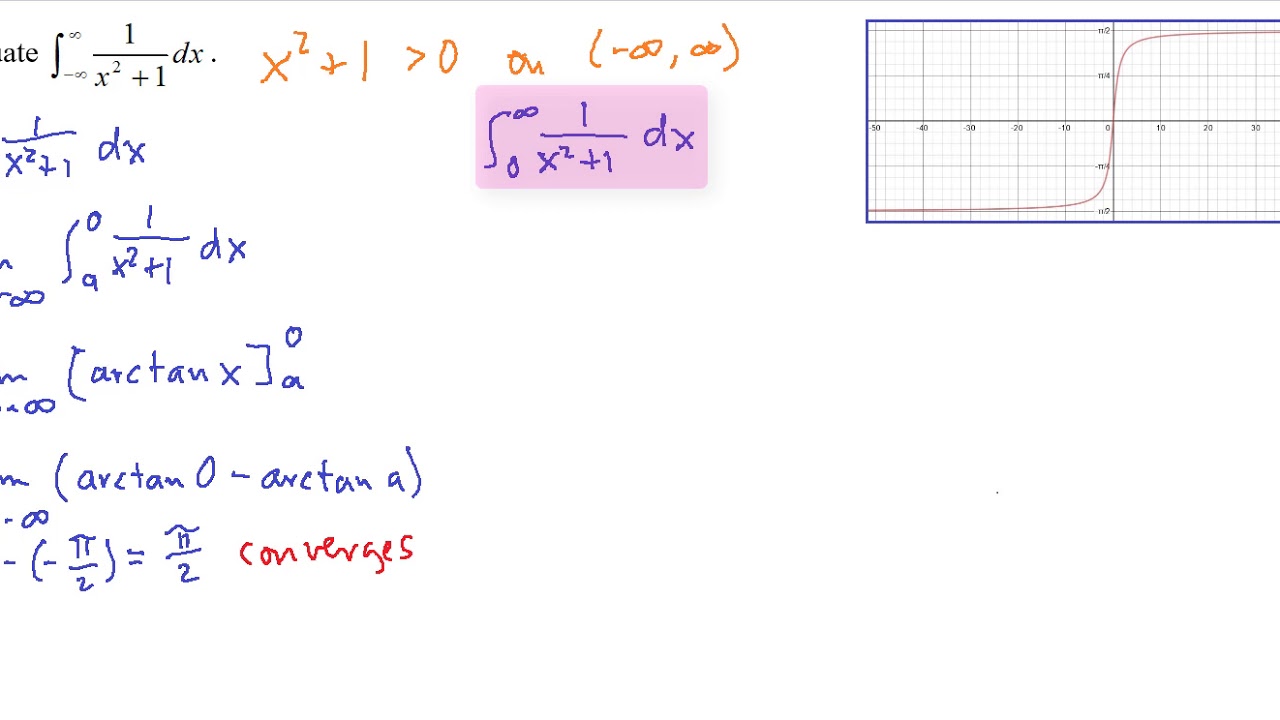



Improper Integrals



Free Math Answers Answers Within 24 Hours Step By Step Explanations




If X 1 A N D F X X 1 X 1 Is A Real Function Then F F F 2 Is A 1 B 2 C 3 D 4




D 1 E 30 1 Iff X X 2x 1 Then F 2 A Chegg Com
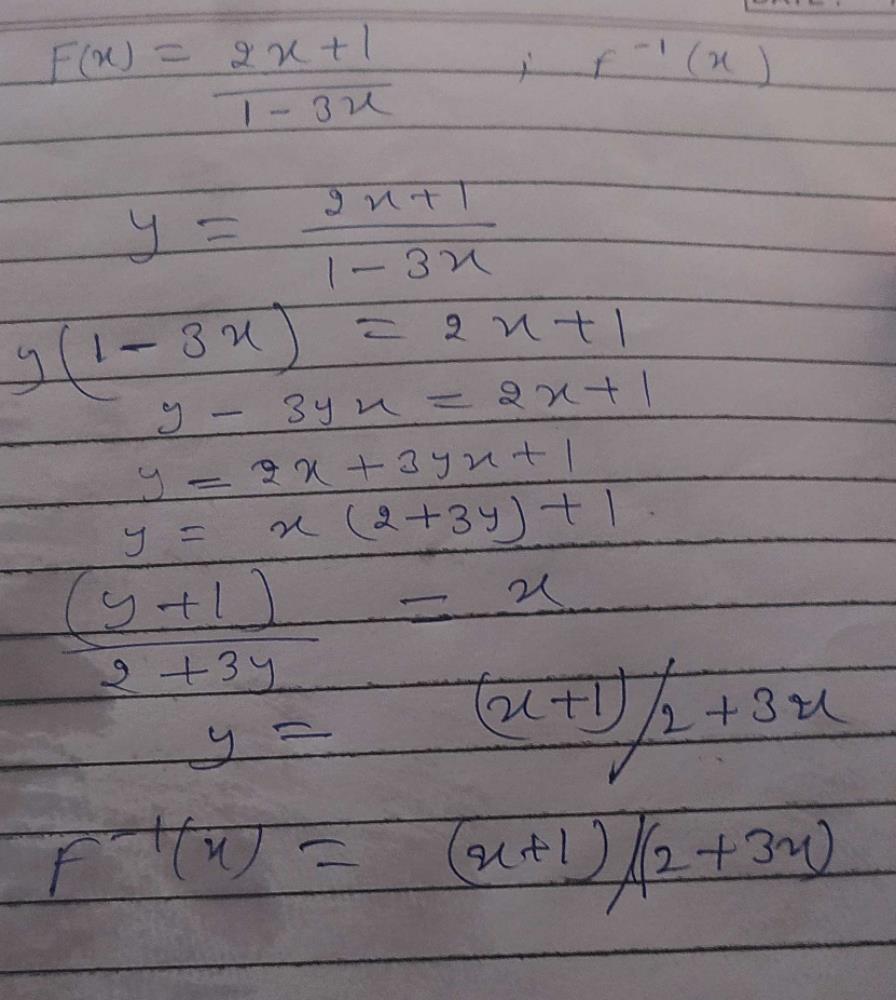



Let The Function F Be Defined By F X 2x 1 1 3x Then F1 X Isa X 1 3x 2b 3x 2 X 1c X 1 3x 2d 2x 1 1 3xcorrect



Www Math Colostate Edu Clayton Teaching M113f10 Homework Hw9solutions Pdf




If The Function F R R Defined By F X 4 X4 X 2 Then Show That F 1 X 1 F X And Hence Deduce The Value Of F 14 2f 12 F 34



Mcetonline Com Wp Content Uploads 21 08 Keam Paper 2 Maths Pdf
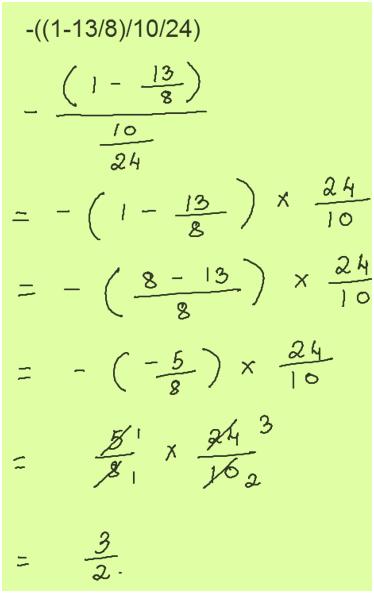



Free Math Answers Answers Within 24 Hours Step By Step Explanations



Asymptotes



Systems Of Linear Equations




Finding Inverse Functions Quadratic Example 2 Video Khan Academy



Inverse Functions




If F X Log 1 X 1 X Then F 2x 1 X 2 Is Equal To




If F X X 1 X 1 Then F 2x Is Equal To Maths Relations And Functions Meritnation Com




D 1 E 30 1 Iff X X 2x 1 Then F 2 A Chegg Com



Www Jstor Org Stable 10 4169 Math Mag 86 1 048




1 Functions




Let The Function F Be Defined By F X 2x 1 1 3x Then F 1 X Is



Math Scene Equations Iii Lesson 3 Quadratic Equations



2



How To Solve F X Log 1 X 1 X And Then F 2x 1 X 2 Quora



Irp Cdn Multiscreensite Com C0cc1c10 Files Uploaded Maths Functions Pdf




If F X X 1 X 1 Find F 2x In Terms Of F X



Www Portnet Org Cms Lib6 Ny Centricity Domain 276 1st and 2nd derivative test 1 Pdf




Taylor Series Wikipedia




Chapter 1 Functions



Http Www Math Sci Hokudai Ac Jp S Settepanella Teachingfile Calculus Calculus2 Pagine Lineintex Pdf




Rd Sharma Solutions For Class 11 Maths Updated For 21 22 Chapter 3 Functions




If F X 2x 3 G X X 3 5 Then Find Fog And Show That Fog Is



Www Nextgurukul In Questions Answers Forum Question Academic If 2x3y6 Z Then 1x1y1z Is Equal To



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿